QT多线程之QtConcurrent::run()
QT有几种可以实现多线程编程的方式,其中最方便使用,最便携的一定是QtConcurrent::run()了,这是一个模板函数,有很多的重载原型。
//在新的线程中调用普通函数 template <typename T> QFuture<T> QtConcurrent::run(Function function, ...) //使用线程池中的线程调用普通函数 template <typename T> QFuture<T> QtConcurrent::run(QThreadPool *pool, Function function, ...) //在新的线程里调用成员函数 有多个重载实现不同的参数个数 template <typename T> QFuture<T> QtConcurrent::run(className *obejct, Function function, ...)
这些模板都有多个重载,支持带参数函数,切可以带多个参数。
QFuture 也是一个模板类,它可以监控线程的运行状态有,并可以获取在另一个线程中运行的函数的返回值,返回值通过调用result()函数获取。
需要注意的是获取返回值之前,最好先调用waitForFinished()保证线程执行完毕。
示例
.h文件
#pragma once
#include <QtCore/QObject>
#include <QtConcurrent/QtConcurrent>
#include <QtCore/QThread>
class ThreadTest {
public:
ThreadTest();
~ThreadTest() = default;
public:
void anotherThread();
std::string anotherThreadReturn();
};
.cpp
#include "QtThreadTest.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <QFuture>
void normalFunction() {
std::cerr << "Normal function thread ID: " << QThread::currentThreadId() << std::endl;
}
ThreadTest::ThreadTest()
{
std::cerr << "main thread ID: " << QThread::currentThreadId() << std::endl;
QtConcurrent::run(normalFunction);
QFuture<void> future = QtConcurrent::run(this, &ThreadTest::anotherThread);
QFuture<std::string> future1 = QtConcurrent::run(this, &ThreadTest::anotherThreadReturn);
future.waitForFinished();
future1.waitForFinished();
std::cerr << "anotherThreadReturn result: " << future1.result() << std::endl;
}
void ThreadTest::anotherThread()
{
std::cerr << "Another thread ID: " << QThread::currentThreadId() << std::endl;
}
std::string ThreadTest::anotherThreadReturn()
{
std::cerr << "Another return thread ID: " << QThread::currentThreadId() << std::endl;
return "This is result";
}
新建对象后的输出结果:
main thread ID: 000000000000499C
Normal function thread ID: 0000000000007830
Another thread ID: 0000000000006BA4
Another return thread ID: 0000000000000A2C
anotherThreadReturn result: This is result
总结
- 调用run() 之后,函数不一定会被立即执行,如果有多个run()被调用,函数的调用顺序不一定是run()的调用顺序,这些都和线程的调度有关系。
- run(function) 实际上等价于run(QThreadPool::globalInstance(),function)
如果只是简单的想在其他线程中调用某个函数,不需要复杂的数据同步,那么QtConcurrent::run() 相比其他实现多线程的方式绝对是不二之选。
2022-11-1 补充
之前因为看漏了文档,导致今天被自己坑了一把。
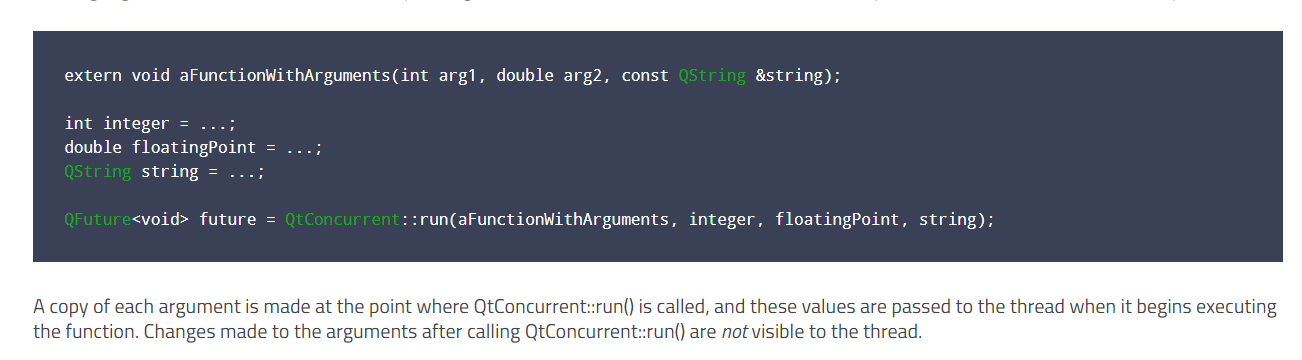
文档中提到,Run中的函数参数,都是拷贝之后使用副本,如果在线程中调用的函数参数类型是引用类型,那么是不能正常对原有的变量进行改变的。
比如下面的例子
void refrencesPar(int& a, int& b)
{
a = 1;
b = 1;
std::cerr << "call refrencesPar() " << "a : " << a << ",b: " << b <<
" |a address:" << &a << " |b address: " << &b <<std::endl;
}
ThreadTest::ThreadTest()
{
int a = 0, b = 0;
auto future = QtConcurrent::run(refrencesPar, a, b);
future.waitForFinished();
std::cerr << "a : " << a << ",b: " << b <<
" |a address:" << &a << " |b address: " << &b << std::endl;
}
运行代码输出的结果:

可以看到,两次输出的a,b变量的地址是不一样的,因为run在调用函数之前已经拷贝了一份副本,所以如果想在函数中改变外面变量的值,这里只能使用指针。
文章评论